Js Web Scraping
- In this video we will take a look at the Node.js library, Cheerio which is a jQuery like tool for the server used in web scraping. This is similar to the pyt.
- Mar 02, 2021 While this article tackles the main aspects of web scraping with NodeJS, it does not talk about web scraping without getting blocked. If you want to learn how to avoid getting blocked, read our complete guide, and if you don't want to deal with this, you can always use our web scraping API.
Part one of this series focuses on requesting and wrangling HTML using two of the most popular Python libraries for web scraping: requests and BeautifulSoup
After the 2016 election I became much more interested in media bias and the manipulation of individuals through advertising. This series will be a walkthrough of a web scraping project that monitors political news from both left and right wing media outlets and performs an analysis on the rhetoric being used, the ads being displayed, and the sentiment of certain topics.
Write a Node.js script to scrape multiple pages; Case 2 – Server-side Rendered HTML. Find the HTML with the data; Write a Node.js script to scrape the page; Case 3 – JavaScript Rendered HTML. Write a Node.js script to scrape the page after running JavaScript; That's a wrap.
The first part of the series will we be getting media bias data and focus on only working locally on your computer, but if you wish to learn how to deploy something like this into production, feel free to leave a comment and let me know.
You should already know:
- Python fundamentals - lists, dicts, functions, loops - learn on Coursera
- Basic HTML
You will have learned:
- Requesting web pages
- Parsing HTML
- Saving and loading scraped data
- Scraping multiple pages in a row
Every time you load a web page you're making a request to a server, and when you're just a human with a browser there's not a lot of damage you can do. With a Python script that can execute thousands of requests a second if coded incorrectly, you could end up costing the website owner a lot of money and possibly bring down their site (see Denial-of-service attack (DoS)).
With this in mind, we want to be very careful with how we program scrapers to avoid crashing sites and causing damage. Every time we scrape a website we want to attempt to make only one request per page. We don't want to be making a request every time our parsing or other logic doesn't work out, so we need to parse only after we've saved the page locally.
If I'm just doing some quick tests, I'll usually start out in a Jupyter notebook because you can request a web page in one cell and have that web page available to every cell below it without making a new request. Since this article is available as a Jupyter notebook, you will see how it works if you choose that format.
After we make a request and retrieve a web page's content, we can store that content locally with Python's open() function. To do so we need to use the argument wb, which stands for 'write bytes'. This let's us avoid any encoding issues when saving.
Below is a function that wraps the open() function to reduce a lot of repetitive coding later on:
Assume we have captured the HTML from google.com in html, which you'll see later how to do. After running this function we will now have a file in the same directory as this notebook called google_com that contains the HTML.
To retrieve our saved file we'll make another function to wrap reading the HTML back into html. We need to use rb for 'read bytes' in this case.
The open function is doing just the opposite: read the HTML from google_com. If our script fails, notebook closes, computer shuts down, etc., we no longer need to request Google again, lessening our impact on their servers. While it doesn't matter much with Google since they have a lot of resources, smaller sites with smaller servers will benefit from this.
I save almost every page and parse later when web scraping as a safety precaution.
Each site usually has a robots.txt on the root of their domain. This is where the website owner explicitly states what bots are allowed to do on their site. Simply go to example.com/robots.txt and you should find a text file that looks something like this:
The User-agent field is the name of the bot and the rules that follow are what the bot should follow. Some robots.txt will have many User-agents with different rules. Common bots are googlebot, bingbot, and applebot, all of which you can probably guess the purpose and origin of.
We don't really need to provide a User-agent when scraping, so User-agent: * is what we would follow. A * means that the following rules apply to all bots (that's us).
The Crawl-delay tells us the number of seconds to wait before requests, so in this example we need to wait 10 seconds before making another request.
Allow gives us specific URLs we're allowed to request with bots, and vice versa for Disallow. In this example we're allowed to request anything in the /pages/subfolder which means anything that starts with example.com/pages/. On the other hand, we are disallowed from scraping anything from the /scripts/subfolder.
Many times you'll see a * next to Allow or Disallow which means you are either allowed or not allowed to scrape everything on the site.
Sometimes there will be a disallow all pages followed by allowed pages like this:
This means that you're not allowed to scrape anything except the subfolder /pages/. Essentially, you just want to read the rules in order where the next rule overrides the previous rule.
This project will primarily be run through a Jupyter notebook, which is done for teaching purposes and is not the usual way scrapers are programmed. After showing you the pieces, we'll put it all together into a Python script that can be run from command line or your IDE of choice.
With Python's requests (pip install requests) library we're getting a web page by using get() on the URL. The response r contains many things, but using r.content will give us the HTML. Once we have the HTML we can then parse it for the data we're interested in analyzing.
There's an interesting website called AllSides that has a media bias rating table where users can agree or disagree with the rating.
Since there's nothing in their robots.txt that disallows us from scraping this section of the site, I'm assuming it's okay to go ahead and extract this data for our project. Let's request the this first page:
Since we essentially have a giant string of HTML, we can print a slice of 100 characters to confirm we have the source of the page. Let's start extracting data.
What does BeautifulSoup do?
We used requests to get the page from the AllSides server, but now we need the BeautifulSoup library (pip install beautifulsoup4) to parse HTML and XML. When we pass our HTML to the BeautifulSoup constructor we get an object in return that we can then navigate like the original tree structure of the DOM.
This way we can find elements using names of tags, classes, IDs, and through relationships to other elements, like getting the children and siblings of elements.
We create a new BeautifulSoup object by passing the constructor our newly acquired HTML content and the type of parser we want to use:
This soup object defines a bunch of methods — many of which can achieve the same result — that we can use to extract data from the HTML. Let's start with finding elements.
To find elements and data inside our HTML we'll be using select_one, which returns a single element, and select, which returns a list of elements (even if only one item exists). Both of these methods use CSS selectors to find elements, so if you're rusty on how CSS selectors work here's a quick refresher:
A CSS selector refresher
- To get a tag, such as
<a></a>,<body></body>, use the naked name for the tag. E.g.select_one('a')gets an anchor/link element,select_one('body')gets the body element .tempgets an element with a class of temp, E.g. to get<a></a>useselect_one('.temp')#tempgets an element with an id of temp, E.g. to get<a></a>useselect_one('#temp').temp.examplegets an element with both classes temp and example, E.g. to get<a></a>useselect_one('.temp.example').temp agets an anchor element nested inside of a parent element with class temp, E.g. to get<div><a></a></div>useselect_one('.temp a'). Note the space between.tempanda..temp .examplegets an element with class example nested inside of a parent element with class temp, E.g. to get<div><a></a></div>useselect_one('.temp .example'). Again, note the space between.tempand.example. The space tells the selector that the class after the space is a child of the class before the space.- ids, such as
<a id=one></a>, are unique so you can usually use the id selector by itself to get the right element. No need to do nested selectors when using ids.
There's many more selectors for for doing various tasks, like selecting certain child elements, specific links, etc., that you can look up when needed. The selectors above get us pretty close to everything we would need for now.
Tips on figuring out how to select certain elements
Most browsers have a quick way of finding the selector for an element using their developer tools. In Chrome, we can quickly find selectors for elements by
- Right-click on the the element then select 'Inspect' in the menu. Developer tools opens and and highlights the element we right-clicked
- Right-click the code element in developer tools, hover over 'Copy' in the menu, then click 'Copy selector'
Sometimes it'll be a little off and we need to scan up a few elements to find the right one. Here's what it looks like to find the selector and Xpath, another type of selector, in Chrome:
Our data is housed in a table on AllSides, and by inspecting the header element we can find the code that renders the table and rows. What we need to do is select all the rows from the table and then parse out the information from each row.
Here's how to quickly find the table in the source code:
Simplifying the table's HTML, the structure looks like this (comments <!-- --> added by me):
So to get each row, we just select all <tr> inside <tbody>:
tbody tr tells the selector to extract all <tr> (table row) tags that are children of the <tbody> body tag. If there were more than one table on this page we would have to make a more specific selector, but since this is the only table, we're good to go.
Now we have a list of HTML table rows that each contain four cells:
- News source name and link
- Bias data
- Agreement buttons
- Community feedback data
Below is a breakdown of how to extract each one.
The outlet name (ABC News) is the text of an anchor tag that's nested inside a <td> tag, which is a cell — or table data tag.
Getting the outlet name is pretty easy: just get the first row in rows and run a select_one off that object:
The only class we needed to use in this case was .source-title since .views-field looks to be just a class each row is given for styling and doesn't provide any uniqueness.
Notice that we didn't need to worry about selecting the anchor tag a that contains the text. When we use .text is gets all text in that element, and since 'ABC News' is the only text, that's all we need to do. Bear in mind that using select or select_one will give you the whole element with the tags included, so we need .text to give us the text between the tags.
.strip() ensures all the whitespace surrounding the name is removed. Many websites use whitespace as a way to visually pad the text inside elements so using strip() is always a good idea.
You'll notice that we can run BeautifulSoup methods right off one of the rows. That's because the rows become their own BeautifulSoup objects when we make a select from another BeautifulSoup object. On the other hand, our name variable is no longer a BeautifulSoup object because we called .text.
We also need the link to this news source's page on AllSides. If we look back at the HTML we'll see that in this case we do want to select the anchor in order to get the href that contains the link, so let's do that:
It is a relative path in the HTML, so we prepend the site's URL to make it a link we can request later.
Getting the link was a bit different than just selecting an element. We had to access an attribute (href) of the element, which is done using brackets, like how we would access a Python dictionary. This will be the same for other attributes of elements, like src in images and videos.
We can see that the rating is displayed as an image so how can we get the rating in words? Looking at the HTML notice the link that surrounds the image has the text we need:
We could also pull the alt attribute, but the link looks easier. Let's grab it:
Here we selected the anchor tag by using the class name and tag together: .views-field-field-bias-image is the class of the <td> and <a> is for the anchor nested inside.
After that we extract the href just like before, but now we only want the last part of the URL for the name of the bias so we split on slashes and get the last element of that split (left-center).
The last thing to scrape is the agree/disagree ratio from the community feedback area. The HTML of this cell is pretty convoluted due to the styling, but here's the basic structure:
The numbers we want are located in two span elements in the last div. Both span elements have classes that are unique in this cell so we can use them to make the selection:
Using .text will return a string, so we need to convert them to integers in order to calculate the ratio.
Side note: If you've never seen this way of formatting print statements in Python, the f at the front allows us to insert variables right into the string using curly braces. The :.2f is a way to format floats to only show two decimals places.
If you look at the page in your browser you'll notice that they say how much the community is in agreement by using 'somewhat agree', 'strongly agree', etc. so how do we get that? If we try to select it:
It shows up as None because this element is rendered with Javascript and requests can't pull HTML rendered with Javascript. We'll be looking at how to get data rendered with JS in a later article, but since this is the only piece of information that's rendered this way we can manually recreate the text.
To find the JS files they're using, just CTRL+F for '.js' in the page source and open the files in a new tab to look for that logic.
It turned out the logic was located in the eleventh JS file and they have a function that calculates the text and color with these parameters:
| Range | Agreeance |
| $ratio > 3$ | absolutely agrees |
| $2 < ratio leq 3$ | strongly agrees |
| $1.5 < ratio leq 2$ | agrees |
| $1 < ratio leq 1.5$ | somewhat agrees |
| $ratio = 1$ | neutral |
| $0.67 < ratio < 1$ | somewhat disgrees |
| $0.5 < ratio leq 0.67$ | disgrees |
| $0.33 < ratio leq 0.5$ | strongly disagrees |
| $ratio leq 0.33$ | absolutely disagrees |
Now that we have the general logic for a single row and we can generate the agreeance text, let's create a loop that gets data from every row on the first page:
In the loop we can combine any multi-step extractions into one to create the values in the least number of steps.
Our data list now contains a dictionary containing key information for every row.
Keep in mind that this is still only the first page. The list on AllSides is three pages long as of this writing, so we need to modify this loop to get the other pages.
Notice that the URLs for each page follow a pattern. The first page has no parameters on the URL, but the next pages do; specifically they attach a ?page=#to the URL where '#' is the page number.
Right now, the easiest way to get all pages is just to manually make a list of these three pages and loop over them. If we were working on a project with thousands of pages we might build a more automated way of constructing/finding the next URLs, but for now this works.
According to AllSides' robots.txt we need to make sure we wait ten seconds before each request.
Our loop will:
- request a page
- parse the page
- wait ten seconds
- repeat for next page.
Remember, we've already tested our parsing above on a page that was cached locally so we know it works. You'll want to make sure to do this before making a loop that performs requests to prevent having to reloop if you forgot to parse something.
By combining all the steps we've done up to this point and adding a loop over pages, here's how it looks:
Now we have a list of dictionaries for each row on all three pages.
To cap it off, we want to get the real URL to the news source, not just the link to their presence on AllSides. To do this, we will need to get the AllSides page and look for the link.
If we go to ABC News' page there's a row of external links to Facebook, Twitter, Wikipedia, and the ABC News website. The HTML for that sections looks like this:
Notice the anchor tag (<a>) that contains the link to ABC News has a class of 'www'. Pretty easy to get with what we've already learned:
So let's make another loop to request the AllSides page and get links for each news source. Unfortunately, some pages don't have a link in this grey bar to the news source, which brings up a good point: always account for elements to randomly not exist.
Up until now we've assumed elements exist in the tables we scraped, but it's always a good idea to program scrapers in way so they don't break when an element goes missing.
Using select_one or select will always return None or an empty list if nothing is found, so in this loop we'll check if we found the website element or not so it doesn't throw an Exception when trying to access the href attribute.
Finally, since there's 265 news source pages and the wait time between pages is 10 seconds, it's going to take ~44 minutes to do this. Instead of blindly not knowing our progress, let's use the tqdm library (pip install tqdm) to give us a nice progress bar:
tqdm is a little weird at first, but essentially tqdm_notebook is just wrapping around our data list to produce a progress bar. We are still able to access each dictionary, d, just as we would normally. Note that tqdm_notebook is only for Jupyter notebooks. In regular editors you'll just import tqdm from tqdm and use tqdm instead.
So what do we have now? At this moment, data is a list of dictionaries, each of which contains all the data from the tables as well as the websites from each individual news source's page on AllSides.
The first thing we'll want to do now is save that data to a file so we don't have to make those requests again. We'll be storing the data as JSON since it's already in that form anyway:
If you're not familiar with JSON, just quickly open allsides.json in an editor and see what it looks like. It should look almost exactly like what data looks like if we print it in Python: a list of dictionaries.
Before ending this article I think it would be worthwhile to actually see what's interesting about this data we just retrieved. So, let's answer a couple of questions.
Which ratings for outlets does the communityabsolutely agreeon?
To find where the community absolutely agrees we can do a simple list comprehension that checks each dict for the agreeance text we want:
Using some string formatting we can make it look somewhat tabular. Interestingly, C-SPAN is the only center bias that the community absolutely agrees on. The others for left and right aren't that surprising.
Which ratings for outlets does the communityabsolutely disagreeon?
To make analysis a little easier, we can also load our JSON data into a Pandas DataFrame as well. This is easy with Pandas since they have a simple function for reading JSON into a DataFrame.
As an aside, if you've never used Pandas (pip install pandas), Matplotlib (pip install matplotlib), or any of the other data science libraries, I would definitely recommend checking out Jose Portilla's data science course for a great intro to these tools and many machine learning concepts.
Now to the DataFrame:
| agree | agree_ratio | agreeance_text | allsides_page | bias | disagree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | ||||||
| ABC News | 8355 | 1.260371 | somewhat agrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/abc-news-... | left-center | 6629 |
| Al Jazeera | 1996 | 0.694986 | somewhat disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/al-jazeer... | center | 2872 |
| AllSides | 2615 | 2.485741 | strongly agrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/allsides-0 | allsides | 1052 |
| AllSides Community | 1760 | 1.668246 | agrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/allsides-... | allsides | 1055 |
| AlterNet | 1226 | 2.181495 | strongly agrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/alternet | left | 562 |
| agree | agree_ratio | agreeance_text | allsides_page | bias | disagree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | ||||||
| CNBC | 1239 | 0.398905 | strongly disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/cnbc | center | 3106 |
| Quillette | 45 | 0.416667 | strongly disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/quillette... | right-center | 108 |
| The Courier-Journal | 64 | 0.410256 | strongly disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/courier-j... | left-center | 156 |
| The Economist | 779 | 0.485964 | strongly disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/economist | left-center | 1603 |
| The Observer (New York) | 123 | 0.484252 | strongly disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/observer | center | 254 |
| The Oracle | 33 | 0.485294 | strongly disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/oracle | center | 68 |
| The Republican | 108 | 0.392727 | strongly disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/republican | center | 275 |
It looks like much of the community disagrees strongly with certain outlets being rated with a 'center' bias.
Let's make a quick visualization of agreeance. Since there's too many news sources to plot so let's pull only those with the most votes. To do that, we can make a new column that counts the total votes and then sort by that value:
| agree | agree_ratio | agreeance_text | allsides_page | bias | disagree | total_votes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | |||||||
| CNN (Web News) | 22907 | 0.970553 | somewhat disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/cnn-media... | left-center | 23602 | 46509 |
| Fox News | 17410 | 0.650598 | disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/fox-news-... | right-center | 26760 | 44170 |
| Washington Post | 21434 | 1.682022 | agrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/washingto... | left-center | 12743 | 34177 |
| New York Times - News | 12275 | 0.570002 | disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/new-york-... | left-center | 21535 | 33810 |
| HuffPost | 15056 | 0.834127 | somewhat disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/huffpost-... | left | 18050 | 33106 |
| Politico | 11047 | 0.598656 | disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/politico-... | left-center | 18453 | 29500 |
| Washington Times | 18934 | 2.017475 | strongly agrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/washingto... | right-center | 9385 | 28319 |
| NPR News | 15751 | 1.481889 | somewhat agrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/npr-media... | center | 10629 | 26380 |
| Wall Street Journal - News | 9872 | 0.627033 | disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/wall-stre... | center | 15744 | 25616 |
| Townhall | 7632 | 0.606967 | disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/townhall-... | right | 12574 | 20206 |
Visualizing the data
To make a bar plot we'll use Matplotlib with Seaborn's dark grid style:
As mentioned above, we have too many news outlets to plot comfortably, so just make a copy of the top 25 and place it in a new df2 variable:
| agree | agree_ratio | agreeance_text | allsides_page | bias | disagree | total_votes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | |||||||
| CNN (Web News) | 22907 | 0.970553 | somewhat disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/cnn-media... | left-center | 23602 | 46509 |
| Fox News | 17410 | 0.650598 | disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/fox-news-... | right-center | 26760 | 44170 |
| Washington Post | 21434 | 1.682022 | agrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/washingto... | left-center | 12743 | 34177 |
| New York Times - News | 12275 | 0.570002 | disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/new-york-... | left-center | 21535 | 33810 |
| HuffPost | 15056 | 0.834127 | somewhat disagrees | https://www.allsides.com/news-source/huffpost-... | left | 18050 | 33106 |
With the top 25 news sources by amount of feedback, let's create a stacked bar chart where the number of agrees are stacked on top of the number of disagrees. This makes the total height of the bar the total amount of feedback.
Below, we first create a figure and axes, plot the agree bars, plot the disagree bars on top of the agrees using bottom, then set various text features:
For a slightly more complex version, let's make a subplot for each bias and plot the respective news sources.
This time we'll make a new copy of the original DataFrame beforehand since we can plot more news outlets now.
Instead of making one axes, we'll create a new one for each bias to make six total subplots:
Hopefully the comments help with how these plots were created. We're just looping through each unique bias and adding a subplot to the figure.
When interpreting these plots keep in mind that the y-axis has different scales for each subplot. Overall it's a nice way to see which outlets have a lot of votes and where the most disagreement is. This is what makes scraping so much fun!
We have the tools to make some fairly complex web scrapers now, but there's still the issue with Javascript rendering. This is something that deserves its own article, but for now we can do quite a lot.
There's also some project organization that needs to occur when making this into a more easily runnable program. We need to pull it out of this notebook and code in command-line arguments if we plan to run it often for updates.
These sorts of things will be addressed later when we build more complex scrapers, but feel free to let me know in the comments of anything in particular you're interested in learning about.
Resources
Web Scraping with Python: Collecting More Data from the Modern Web — Book on Amazon
Jose Portilla's Data Science and ML Bootcamp — Course on Udemy
Easiest way to get started with Data Science. Covers Pandas, Matplotlib, Seaborn, Scikit-learn, and a lot of other useful topics.
Get updates in your inbox
Join over 7,500 data science learners.
Meet the Authors
Javascript has become one of the most popular and widely used languages due to the massive improvements it has seen and the introduction of the runtime known as NodeJS. Whether it's a web or mobile application, Javascript now has the right tools. This article will explain how the vibrant ecosystem of NodeJS allows you to efficiently scrape the web to meet most of your requirements.
Prerequisites
This post is primarily aimed at developers who have some level of experience with Javascript. However, if you have a firm understanding of Web Scraping but have no experience with Javascript, this post could still prove useful.Below are the recommended prerequisites for this article:
- ✅ Experience with Javascript
- ✅ Experience using DevTools to extract selectors of elements
- ✅ Some experience with ES6 Javascript (Optional)
⭐ Make sure to check out the resources at the end of this article to learn more!
Outcomes
After reading this post will be able to:
- Have a functional understanding of NodeJS
- Use multiple HTTP clients to assist in the web scraping process
- Use multiple modern and battle-tested libraries to scrape the web
Understanding NodeJS: A brief introduction
Javascript is a simple and modern language that was initially created to add dynamic behavior to websites inside the browser. When a website is loaded, Javascript is run by the browser's Javascript Engine and converted into a bunch of code that the computer can understand.
For Javascript to interact with your browser, the browser provides a Runtime Environment (document, window, etc.).
This means that Javascript is not the kind of programming language that can interact with or manipulate the computer or it's resources directly. Servers, on the other hand, are capable of directly interacting with the computer and its resources, which allows them to read files or store records in a database.
When introducing NodeJS, the crux of the idea was to make Javascript capable of running not only client-side but also server-side. To make this possible, Ryan Dahl, a skilled developer took Google Chrome's v8 Javascript Engine and embedded it with a C++ program named Node.
So, NodeJS is a runtime environment that allows an application written in Javascript to be run on a server as well.
As opposed to how most languages, including C and C++, deal with concurrency, which is by employing multiple threads, NodeJS makes use of a single main thread and utilizes it to perform tasks in a non-nlocking manner with the help of the Event Loop.
Putting up a simple web server is fairly simple as shown below:
If you have NodeJS installed and you run the above code by typing(without the < and >) in node <YourFileNameHere>.js opening up your browser, and navigating to localhost:3000, you will see some text saying, “Hello World”. NodeJS is ideal for applications that are I/O intensive.
HTTP clients: querying the web
HTTP clients are tools capable of sending a request to a server and then receiving a response from it. Almost every tool that will be discussed in this article uses an HTTP client under the hood to query the server of the website that you will attempt to scrape.
Request
Request is one of the most widely used HTTP clients in the Javascript ecosystem. However, currently, the author of the Request library has officially declared that it is deprecated. This does not mean it is unusable. Quite a lot of libraries still use it, and it is every bit worth using.
It is fairly simple to make an HTTP request with Request:
You can find the Request library at GitHub, and installing it is as simple as running npm install request.
You can also find the deprecation notice and what this means here. If you don't feel safe about the fact that this library is deprecated, there are other options down below!
Axios
Axios is a promise-based HTTP client that runs both in the browser and NodeJS. If you use TypeScript, then Axios has you covered with built-in types.
Making an HTTP request with Axios is straight-forward. It ships with promise support by default as opposed to utilizing callbacks in Request:
If you fancy the async/await syntax sugar for the promise API, you can do that too. But since top level await is still at stage 3, we will have to make use of an async function instead:
All you have to do is call getForum! You can find the Axios library at Github and installing Axios is as simple as npm install axios.
SuperAgent
Much like Axios, SuperAgent is another robust HTTP client that has support for promises and the async/await syntax sugar. It has a fairly straightforward API like Axios, but SuperAgent has more dependencies and is less popular.
Regardless, making an HTTP request with Superagent using promises, async/await, or callbacks looks like this:
You can find the SuperAgent library at GitHub and installing Superagent is as simple as npm install superagent.
For the upcoming few web scraping tools, Axios will be used as the HTTP client.
Note that there are other great HTTP clients for web scrapinglike node-fetch!
Regular expressions: the hard way
The simplest way to get started with web scraping without any dependencies is to use a bunch of regular expressions on the HTML string that you fetch using an HTTP client. But there is a big tradeoff. Regular expressions aren't as flexible and both professionals and amateurs struggle with writing them correctly.
For complex web scraping, the regular expression can also get out of hand. With that said, let's give it a go. Say there's a label with some username in it, and we want the username. This is similar to what you'd have to do if you relied on regular expressions:
In Javascript, match() usually returns an array with everything that matches the regular expression. In the second element(in index 1), you will find the textContent or the innerHTML of the <label>tag which is what we want. But this result contains some unwanted text (“Username: “), which has to be removed.
As you can see, for a very simple use case the steps and the work to be done are unnecessarily high. This is why you should rely on something like an HTML parser, which we will talk about next.
Cheerio: Core jQuery for traversing the DOM
Cheerio is an efficient and light library that allows you to use the rich and powerful API of jQuery on the server-side. If you have used jQuery previously, you will feel right at home with Cheerio. It removes all of the DOM inconsistencies and browser-related features and exposes an efficient API to parse and manipulate the DOM.
As you can see, using Cheerio is similar to how you'd use jQuery.
However, it does not work the same way that a web browser works, which means it does not:

- Render any of the parsed or manipulated DOM elements
- Apply CSS or load any external resource
- Execute Javascript
So, if the website or web application that you are trying to crawl is Javascript-heavy (for example a Single Page Application), Cheerio is not your best bet. You might have to rely on other options mentionned later in this article.
To demonstrate the power of Cheerio, we will attempt to crawl the r/programming forum in Reddit and, get a list of post names.
First, install Cheerio and axios by running the following command:npm install cheerio axios.
Then create a new file called crawler.js, and copy/paste the following code:
getPostTitles() is an asynchronous function that will crawl the Reddit's old r/programming forum. First, the HTML of the website is obtained using a simple HTTP GET request with the axios HTTP client library. Then the HTML data is fed into Cheerio using the cheerio.load() function.
With the help of the browser Dev-Tools, you can obtain the selector that is capable of targeting all of the postcards. If you've used jQuery, the $('div > p.title > a') is probably familiar. This will get all the posts. Since you only want the title of each post individually, you have to loop through each post. This is done with the help of the each() function.
To extract the text out of each title, you must fetch the DOM element with the help of Cheerio (el refers to the current element). Then, calling text() on each element will give you the text.
Now, you can pop open a terminal and run node crawler.js. You'll then see an array of about 25 or 26 different post titles (it'll be quite long). While this is a simple use case, it demonstrates the simple nature of the API provided by Cheerio.
If your use case requires the execution of Javascript and loading of external sources, the following few options will be helpful.
JSDOM: the DOM for Node
JSDOM is a pure Javascript implementation of the Document Object Model to be used in NodeJS. As mentioned previously, the DOM is not available to Node, so JSDOM is the closest you can get. It more or less emulates the browser.
Once a DOM is created, it is possible to interact with the web application or website you want to crawl programmatically, so something like clicking on a button is possible. If you are familiar with manipulating the DOM, using JSDOM will be straightforward.
As you can see, JSDOM creates a DOM. Then you can manipulate this DOM with the same methods and properties you would use while manipulating the browser DOM.
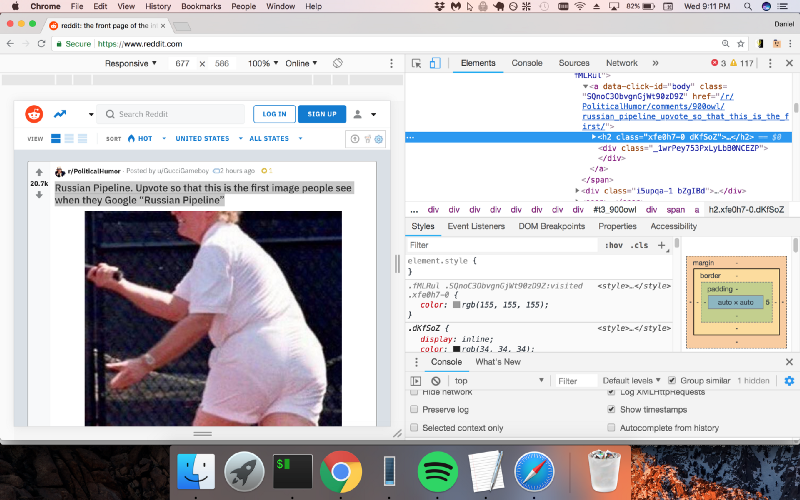
To demonstrate how you could use JSDOM to interact with a website, we will get the first post of the Reddit r/programming forum and upvote it. Then, we will verify if the post has been upvoted.
Start by running the following command to install JSDOM and Axios:npm install jsdom axios
Then, make a file named crawler.js and copy/paste the following code:
upvoteFirstPost() is an asynchronous function that will obtain the first post in r/programming and upvote it. To do this, axios sends an HTTP GET request to fetch the HTML of the URL specified. Then a new DOM is created by feeding the HTML that was fetched earlier.
Js Web Scraping Software
The JSDOM constructor accepts the HTML as the first argument and the options as the second. The two options that have been added perform the following functions:
- runScripts: When set to “dangerously”, it allows the execution of event handlers and any Javascript code. If you do not have a clear idea of the credibility of the scripts that your application will run, it is best to set runScripts to “outside-only”, which attaches all of the Javascript specification provided globals to the
windowobject, thus preventing any script from being executed on the inside. - resources: When set to “usable”, it allows the loading of any external script declared using the
<script>tag (e.g, the jQuery library fetched from a CDN).
Once the DOM has been created, you can use the same DOM methods to get the first post's upvote button and then click on it. To verify if it has been clicked, you could check the classList for a class called upmod. If this class exists in classList, a message is returned.
Node Js Web Scraping Login
Now, you can pop open a terminal and run node crawler.js. You'll then see a neat string that will tell you if the post has been upvoted. While this example use case is trivial, you could build on top of it to create something powerful (for example, a bot that goes around upvoting a particular user's posts).
If you dislike the lack of expressiveness in JSDOM and your crawling relies heavily on such manipulations or if there is a need to recreate many different DOMs, the following options will be a better match.
Puppeteer: the headless browser
Puppeteer, as the name implies, allows you to manipulate the browser programmatically, just like how a puppet would be manipulated by its puppeteer. It achieves this by providing a developer with a high-level API to control a headless version of Chrome by default and can be configured to run non-headless.
Taken from the Puppeteer Docs (Source)
Puppeteer is particularly more useful than the aforementioned tools because it allows you to crawl the web as if a real person were interacting with a browser. This opens up a few possibilities that weren't there before:
- You can get screenshots or generate PDFs of pages.
- You can crawl a Single Page Application and generate pre-rendered content.
- You can automate many different user interactions, like keyboard inputs, form submissions, navigation, etc.
It could also play a big role in many other tasks outside the scope of web crawling like UI testing, assist performance optimization, etc.
Quite often, you will probably want to take screenshots of websites or, get to know about a competitor's product catalog. Puppeteer can be used to do this. To start, install Puppeteer by running the following command:npm install puppeteer
This will download a bundled version of Chromium which takes up about 180 to 300 MB, depending on your operating system. If you wish to disable this and point Puppeteer to an already downloaded version of Chromium, you must set a few environment variables.
This, however, is not recommended. Ff you truly wish to avoid downloading Chromium and Puppeteer for this tutorial, you can rely on the Puppeteer playground.
Let's attempt to get a screenshot and PDF of the r/programming forum in Reddit, create a new file called crawler.js, and copy/paste the following code:
getVisual() is an asynchronous function that will take a screenshot and PDF of the value assigned to the URL variable. To start, an instance of the browser is created by running puppeteer.launch(). Then, a new page is created. This page can be thought of like a tab in a regular browser. Then, by calling page.goto() with the URL as the parameter, the page that was created earlier is directed to the URL specified. Finally, the browser instance is destroyed along with the page.
Once that is done and the page has finished loading, a screenshot and PDF will be taken using page.screenshot() and page.pdf() respectively. You could also listen to the Javascript load event and then perform these actions, which is highly recommended at the production level.
When you run the code type in node crawler.js to the terminal, after a few seconds, you will notice that two files by the names screenshot.jpg and page.pdf have been created.
Also, we've written a complete guide on how to download a file with Puppeteer. You should check it out!
Nightmare: an alternative to Puppeteer
Nightmare is another a high-level browser automation library like Puppeteer. It uses Electron but is said to be roughly twice as fast as it's predecessor PhantomJS and it's more modern.
If you dislike Puppeteer or feel discouraged by the size of the Chromium bundle, Nightmare is an ideal choice. To start, install the Nightmare library by running the following command:npm install nightmare
Once Nightmare has been downloaded, we will use it to find ScrapingBee's website through a Google search. To do so, create a file called crawler.js and copy/paste the following code into it:
First, a Nightmare instance is created. Then, this instance is directed to the Google search engine by calling goto() once it has loaded. The search box is fetched using its selector. Then the value of the search box (an input tag) is changed to “ScrapingBee”.
Web Scraping Node Js
After this is finished, the search form is submitted by clicking on the “Google Search” button. Then, Nightmare is told to wait untill the first link has loaded. Once it has loaded, a DOM method will be used to fetch the value of the href attribute of the anchor tag that contains the link.
Finally, once everything is complete, the link is printed to the console. To run the code, type in node crawler.js to your terminal.
Summary
Node Js Web Scraping
That was a long read! But now you understand the different ways to use NodeJS and it's rich ecosystem of libraries to crawl the web in any way you want. To wrap up, you learned:
- ✅ NodeJS is a Javascript runtime that allow Javascript to be run server-side. It has a non-blocking nature thanks to the Event Loop.
- ✅ HTTP clients such as Axios, SuperAgent, Node fetch and Request are used to send HTTP requests to a server and receive a response.
- ✅ Cheerio abstracts the best out of jQuery for the sole purpose of running it server-side for web crawling but does not execute Javascript code.
- ✅ JSDOM creates a DOM per the standard Javascript specification out of an HTML string and allows you to perform DOM manipulations on it.
- ✅ Puppeteer and Nightmare are high-level browser automation libraries, that allow you to programmatically manipulate web applications as if a real person were interacting with them.
Js Web Scraping Software
While this article tackles the main aspects of web scraping with NodeJS, it does not talk about web scraping without getting blocked.
Js Web Scraping Online
If you want to learn how to avoid getting blocked, read our complete guide, and if you don't want to deal with this, you can always use our web scraping API.
Happy Scraping!
Resources
Would you like to read more? Check these links out:
Js Web Scraping Examples
- NodeJS Website - Contains documentation and a lot of information on how to get started.
- Puppeteer's Docs - Contains the API reference and guides for getting started.
- Playright An alternative to Puppeteer, backed by Microsoft.
- ScrapingBee's Blog - Contains a lot of information about Web Scraping goodies on multiple platforms.
